JRE, JDK, and JVM are all essential components in the Java programming environment, but they serve different purposes:
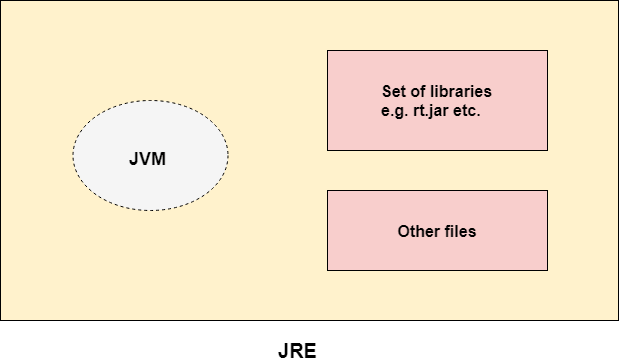
JRE (Java Runtime Environment):
- JRE is the set of software tools that allow a computer to run Java applications.
- It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), class libraries, and other supporting files that are necessary for running Java applications.
- JRE is primarily used by end-users who only need to run Java applications but do not need to develop them.
The implementation of JVM is also actively released by other companies besides Sun Micro Systems.
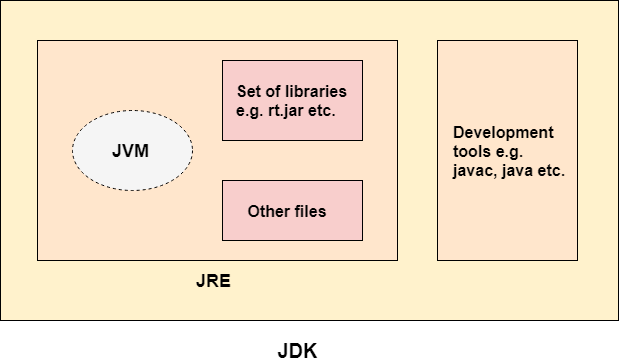
JDK (Java Development Kit):
- JDK is a software development kit used by developers to create Java applications.
- It includes the JRE along with development tools like the Java compiler (Javac), debugger, and other utilities needed for developing Java applications.
- JDK is used by developers for writing, compiling, debugging, and running Java code.
The JDK contains a private Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and a few other resources such as an interpreter/loader (java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (Javadoc), etc. to complete the development of a Java Application.
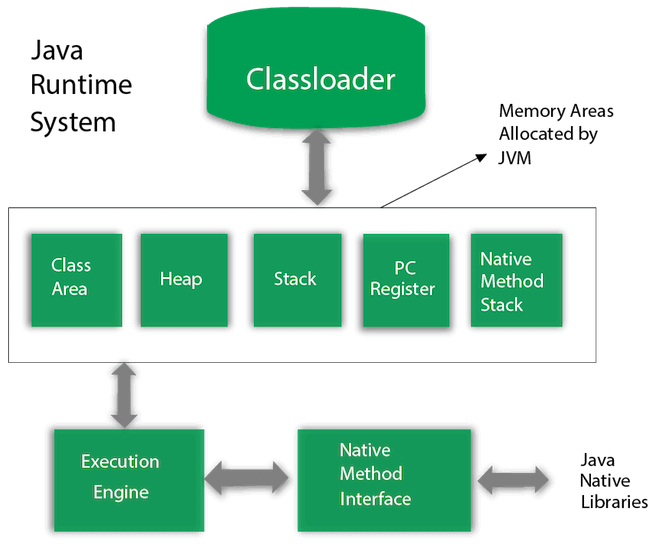
JVM (Java Virtual Machine):
- JVM is an abstract computing machine that provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed.
- It acts as an interpreter for Java bytecode, translating it into machine-specific instructions that can be executed by the underlying hardware.
- JVM is responsible for memory management, garbage collection, and other runtime activities that are essential for executing Java applications.
- It is platform-dependent, meaning different implementations of JVM exist for different operating systems.
In summary, JRE is for running Java applications, JDK is for developing Java applications, and JVM is the runtime environment that executes Java bytecode.
No comments:
Post a Comment